For how many values of k is (x, y) = (k, -k) a solution to the equation 2x +2y = 0?
- A. None
- B. One
- C. Two
- D. More than two
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: D
To determine how many values of \( k \) make \( (x, y) = (k, -k) \) a solution to the equation \( 2x + 2y = 0 \), substitute \( x \) and \( y \) into the equation. This gives \( 2k + 2(-k) = 0 \), which simplifies to \( 0 = 0 \). This statement is always true, meaning any value of \( k \) satisfies the equation. Option A (None) is incorrect; there are indeed solutions. Option B (One) is also wrong since infinitely many values of \( k \) work. Option C (Two) is insufficient, as there are not just two but infinitely many solutions. Hence, the correct interpretation is that there are more than two values of \( k \) that satisfy the equation.
To determine how many values of \( k \) make \( (x, y) = (k, -k) \) a solution to the equation \( 2x + 2y = 0 \), substitute \( x \) and \( y \) into the equation. This gives \( 2k + 2(-k) = 0 \), which simplifies to \( 0 = 0 \). This statement is always true, meaning any value of \( k \) satisfies the equation. Option A (None) is incorrect; there are indeed solutions. Option B (One) is also wrong since infinitely many values of \( k \) work. Option C (Two) is insufficient, as there are not just two but infinitely many solutions. Hence, the correct interpretation is that there are more than two values of \( k \) that satisfy the equation.
Other Related Questions
Malia collected information about whether the members of the 36 households on her block subscribed to cable television and home phone services. Her results are shown in the table below.\nIf a household on Malia's block is selected at random and does subscribe to cable television, what is the probability the members of the household also subscribe to home phone service?
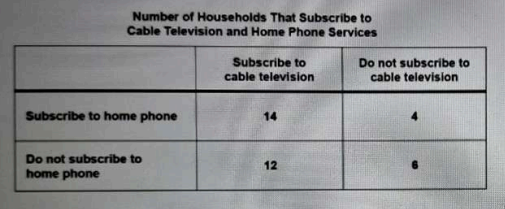
- A. 14/18
- B. 14/26
- C. 18/36
- D. 14/36
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: A
To determine the probability that a household subscribes to home phone service given that it subscribes to cable television, we focus on the relevant subset of households. Malia found 18 households that subscribe to cable, out of which 14 also subscribe to home phone service. Thus, the probability is calculated as the number of households with both services (14) divided by the total number of households with cable (18), resulting in 14/18. Option B (14/26) incorrectly uses the total number of households with home phone service instead of just those with cable. Option C (18/36) misinterprets the probability as a ratio of all households rather than those who subscribe to cable. Option D (14/36) inaccurately represents the total number of households instead of focusing on the cable subscribers.
To determine the probability that a household subscribes to home phone service given that it subscribes to cable television, we focus on the relevant subset of households. Malia found 18 households that subscribe to cable, out of which 14 also subscribe to home phone service. Thus, the probability is calculated as the number of households with both services (14) divided by the total number of households with cable (18), resulting in 14/18. Option B (14/26) incorrectly uses the total number of households with home phone service instead of just those with cable. Option C (18/36) misinterprets the probability as a ratio of all households rather than those who subscribe to cable. Option D (14/36) inaccurately represents the total number of households instead of focusing on the cable subscribers.
Each of the following is a solution to the equation x- 2y = 4 EXCEPT
- A. (-2,-3)
- B. (0,2)
- C. (4,0)
- D. (8,2)
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: B
To determine which option is not a solution to the equation \(x - 2y = 4\), we can substitute each pair into the equation. - For A: \((-2, -3)\), substituting gives \(-2 - 2(-3) = -2 + 6 = 4\), which is correct. - For B: \((0, 2)\), substituting gives \(0 - 2(2) = 0 - 4 = -4\), which does not equal 4, making this option incorrect. - For C: \((4, 0)\), substituting gives \(4 - 2(0) = 4\), which is correct. - For D: \((8, 2)\), substituting gives \(8 - 2(2) = 8 - 4 = 4\), which is correct. Thus, option B is the only pair that does not satisfy the equation.
To determine which option is not a solution to the equation \(x - 2y = 4\), we can substitute each pair into the equation. - For A: \((-2, -3)\), substituting gives \(-2 - 2(-3) = -2 + 6 = 4\), which is correct. - For B: \((0, 2)\), substituting gives \(0 - 2(2) = 0 - 4 = -4\), which does not equal 4, making this option incorrect. - For C: \((4, 0)\), substituting gives \(4 - 2(0) = 4\), which is correct. - For D: \((8, 2)\), substituting gives \(8 - 2(2) = 8 - 4 = 4\), which is correct. Thus, option B is the only pair that does not satisfy the equation.
Square S has area 2√2 square units. What is the length of a side of square S?
- A. ∜128
- B. ∜32
- C. ∜8
- D. ∜2
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: C
To find the length of a side of square S, we use the formula for the area of a square, which is \( \text{Area} = \text{side}^2 \). Given that the area is \( 2\sqrt{2} \), we set up the equation \( \text{side}^2 = 2\sqrt{2} \). Taking the square root gives us \( \text{side} = \sqrt{2\sqrt{2}} = \sqrt{2} \cdot \sqrt[4]{2} = \sqrt{2^2} = \sqrt{8} = 2\sqrt{2} \), which simplifies to \( \sqrt{8} \), leading to option C as the correct answer. Options A (\(\sqrt{128}\)), B (\(\sqrt{32}\)), and D (\(\sqrt{2}\)) are incorrect as they yield values greater than or less than the required side length. Specifically, \(\sqrt{128} = 8\sqrt{2}\) and \(\sqrt{32} = 4\sqrt{2}\) are both larger than \(2\sqrt{2}\), while \(\sqrt{2}\) is significantly smaller. Thus, option C accurately represents the side length of square S.
To find the length of a side of square S, we use the formula for the area of a square, which is \( \text{Area} = \text{side}^2 \). Given that the area is \( 2\sqrt{2} \), we set up the equation \( \text{side}^2 = 2\sqrt{2} \). Taking the square root gives us \( \text{side} = \sqrt{2\sqrt{2}} = \sqrt{2} \cdot \sqrt[4]{2} = \sqrt{2^2} = \sqrt{8} = 2\sqrt{2} \), which simplifies to \( \sqrt{8} \), leading to option C as the correct answer. Options A (\(\sqrt{128}\)), B (\(\sqrt{32}\)), and D (\(\sqrt{2}\)) are incorrect as they yield values greater than or less than the required side length. Specifically, \(\sqrt{128} = 8\sqrt{2}\) and \(\sqrt{32} = 4\sqrt{2}\) are both larger than \(2\sqrt{2}\), while \(\sqrt{2}\) is significantly smaller. Thus, option C accurately represents the side length of square S.
If the length of a rectangle is increased by 30% and the width of the same rectangle is decreased by 30%, what is the effect on the area of the rectangle?
- A. It is increased by 60%.
- B. It is unchanged.
- C. It is decreased by 15%.
- D. It is decreased by 9%.
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: D
Increasing the length of a rectangle by 30% results in a new length of 1.3L, while decreasing the width by 30% gives a new width of 0.7W. The new area can be calculated as A' = (1.3L)(0.7W) = 0.91LW, indicating a decrease in area. Option A is incorrect because a 60% increase does not occur; the area actually decreases. Option B is wrong as the area changes due to the modifications in dimensions. Option C suggests a decrease of 15%, which miscalculates the area change. The area decreases by 9%, confirming the effect of the opposing percentage changes in length and width.
Increasing the length of a rectangle by 30% results in a new length of 1.3L, while decreasing the width by 30% gives a new width of 0.7W. The new area can be calculated as A' = (1.3L)(0.7W) = 0.91LW, indicating a decrease in area. Option A is incorrect because a 60% increase does not occur; the area actually decreases. Option B is wrong as the area changes due to the modifications in dimensions. Option C suggests a decrease of 15%, which miscalculates the area change. The area decreases by 9%, confirming the effect of the opposing percentage changes in length and width.