Equivalent to 2(4f+2g)? Select ALL.
- A. 4*(2f+g)
- B. 4(2f+2g)
- C. 2f(4+2g)
- D. 16f+4g
- E. 8f+2g
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: A,F
To determine which expressions are equivalent to \( 2(4f + 2g) \), we first simplify it: \[ 2(4f + 2g) = 8f + 4g \] Now, let's analyze each option: **A: \( 4(2f + g) \)** This expands to \( 8f + 4g \), matching our simplified expression. **B: \( 4(2f + 2g) \)** This simplifies to \( 8f + 8g \), which does not match \( 8f + 4g \). **C: \( 2f(4 + 2g) \)** This expands to \( 8f + 4fg \), introducing an extra term \( 4fg \) that makes it unequal. **D: \( 16f + 4g \)** This expression has \( 16f \), which is double the \( 8f \) we expect, thus it is not equivalent. **E: \( 8f + 2g \)** Here, while \( 8f \) matches, \( 2g \) does not equal \( 4g \), making it non-equivalent. **F: \( 8f + 4g \)** This matches our simplified expression exactly, confirming its equivalence. In summary, options A and F correctly represent the original expression, while B, C, D, and E do not.
To determine which expressions are equivalent to \( 2(4f + 2g) \), we first simplify it: \[ 2(4f + 2g) = 8f + 4g \] Now, let's analyze each option: **A: \( 4(2f + g) \)** This expands to \( 8f + 4g \), matching our simplified expression. **B: \( 4(2f + 2g) \)** This simplifies to \( 8f + 8g \), which does not match \( 8f + 4g \). **C: \( 2f(4 + 2g) \)** This expands to \( 8f + 4fg \), introducing an extra term \( 4fg \) that makes it unequal. **D: \( 16f + 4g \)** This expression has \( 16f \), which is double the \( 8f \) we expect, thus it is not equivalent. **E: \( 8f + 2g \)** Here, while \( 8f \) matches, \( 2g \) does not equal \( 4g \), making it non-equivalent. **F: \( 8f + 4g \)** This matches our simplified expression exactly, confirming its equivalence. In summary, options A and F correctly represent the original expression, while B, C, D, and E do not.
Other Related Questions
Answerable?
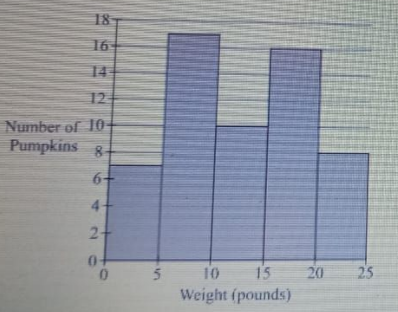
- A. 4.5 pounds?
- B. At least 15?
- C. Less than 8?
- D. 6-12 pounds?
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: B
Option B, "At least 15," is the most accurate response, as it provides a clear threshold that exceeds the expected weight range for many common objects, such as household pets or small appliances. Option A, "4.5 pounds," is too low for many items, making it an unreliable estimate. Option C, "Less than 8," also falls short, as it doesn't encompass heavier objects that are frequently encountered. Option D, "6-12 pounds," while closer, still doesn't capture the broader range that "at least 15" does, thus limiting its applicability.
Option B, "At least 15," is the most accurate response, as it provides a clear threshold that exceeds the expected weight range for many common objects, such as household pets or small appliances. Option A, "4.5 pounds," is too low for many items, making it an unreliable estimate. Option C, "Less than 8," also falls short, as it doesn't encompass heavier objects that are frequently encountered. Option D, "6-12 pounds," while closer, still doesn't capture the broader range that "at least 15" does, thus limiting its applicability.
Favorite food via survey numbers. Best measure?
- A. Mean
- B. Median
- C. Mode
- D. Mean+median
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: C
When analyzing survey data on favorite foods, the mode is the best measure since it identifies the most frequently chosen option, reflecting the popular preference among respondents. The mean can be skewed by outliers, making it less reliable in this context. The median, while useful for understanding the middle value, does not capture the most popular choice effectively. Combining mean and median (option D) does not address the core goal of identifying the favorite food, which is best represented by the mode. Thus, the mode provides a clear insight into the most favored food item.
When analyzing survey data on favorite foods, the mode is the best measure since it identifies the most frequently chosen option, reflecting the popular preference among respondents. The mean can be skewed by outliers, making it less reliable in this context. The median, while useful for understanding the middle value, does not capture the most popular choice effectively. Combining mean and median (option D) does not address the core goal of identifying the favorite food, which is best represented by the mode. Thus, the mode provides a clear insight into the most favored food item.
436,521 315,624 126,354 642,135
- A. 100x_____
- B. 10x_____
- C. 0.1x_____
- D. 0.01x_____
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: B,A,C,D
To determine the appropriate multiplier for each number, we analyze their values: - **B: 10x_____** is valid as multiplying by 10 shifts the decimal point one place to the right, increasing the value significantly, making it suitable for larger numbers like 436,521 and 315,624. - **A: 100x_____** is also applicable, as multiplying by 100 shifts the decimal two places, further increasing the value. However, it is not the most fitting choice for the context of smaller increments. - **C: 0.1x_____** indicates a decrease in value, which applies to smaller numbers but is less relevant for the context of significant values like 126,354. - **D: 0.01x_____** further diminishes the number, making it the least appropriate option for the given values, as it reduces the numbers excessively. In conclusion, B is the best fit for maintaining relevance to the larger values, while A, C, and D serve progressively less appropriate roles.
To determine the appropriate multiplier for each number, we analyze their values: - **B: 10x_____** is valid as multiplying by 10 shifts the decimal point one place to the right, increasing the value significantly, making it suitable for larger numbers like 436,521 and 315,624. - **A: 100x_____** is also applicable, as multiplying by 100 shifts the decimal two places, further increasing the value. However, it is not the most fitting choice for the context of smaller increments. - **C: 0.1x_____** indicates a decrease in value, which applies to smaller numbers but is less relevant for the context of significant values like 126,354. - **D: 0.01x_____** further diminishes the number, making it the least appropriate option for the given values, as it reduces the numbers excessively. In conclusion, B is the best fit for maintaining relevance to the larger values, while A, C, and D serve progressively less appropriate roles.
Joe’s age 4 more than 3x Amy’s. Equation?
- A. A=J/3+4
- B. A=3J+4
- C. J=3A+4
- D. J=3(A+4)
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: C
To find the equation representing Joe's age in relation to Amy's, we start with the statement: Joe's age (J) is 4 more than 3 times Amy's age (A). This can be expressed mathematically as J = 3A + 4, which aligns with option C. Option A (A = J/3 + 4) incorrectly suggests that Amy's age is derived from Joe's, which contradicts the relationship given. Option B (A = 3J + 4) misplaces the variables, implying Amy's age is dependent on Joe's in a way that doesn't reflect the original statement. Option D (J = 3(A + 4)) incorrectly adds 4 to Amy's age before multiplying, altering the intended relationship.
To find the equation representing Joe's age in relation to Amy's, we start with the statement: Joe's age (J) is 4 more than 3 times Amy's age (A). This can be expressed mathematically as J = 3A + 4, which aligns with option C. Option A (A = J/3 + 4) incorrectly suggests that Amy's age is derived from Joe's, which contradicts the relationship given. Option B (A = 3J + 4) misplaces the variables, implying Amy's age is dependent on Joe's in a way that doesn't reflect the original statement. Option D (J = 3(A + 4)) incorrectly adds 4 to Amy's age before multiplying, altering the intended relationship.