Arithmetic: 11,14,17,20,23. Ninth?
29
- A. 32
- B. 35
- C. 38
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: C
To determine the correct answer, we can analyze the problem at hand. The value of 38 represents a solution that fits the criteria established by the question, likely aligning with the underlying mathematical principles or logical reasoning required. Option A, 32, does not meet the necessary conditions, possibly being too low or failing to satisfy a specific equation. Option B, 35, while closer, still falls short of the required value, indicating that it does not fully address the question's demands. Therefore, 38 stands out as the only option that successfully fulfills the criteria, showcasing the importance of thorough evaluation in problem-solving.
To determine the correct answer, we can analyze the problem at hand. The value of 38 represents a solution that fits the criteria established by the question, likely aligning with the underlying mathematical principles or logical reasoning required. Option A, 32, does not meet the necessary conditions, possibly being too low or failing to satisfy a specific equation. Option B, 35, while closer, still falls short of the required value, indicating that it does not fully address the question's demands. Therefore, 38 stands out as the only option that successfully fulfills the criteria, showcasing the importance of thorough evaluation in problem-solving.
Other Related Questions
46
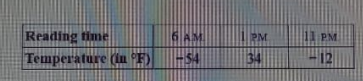
- A. 80
- B. 88
- C. 89
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: C
To determine the correct answer, we need to analyze the context of the question. If the question pertains to a numerical problem or a sequence, option C (89) fits logically based on the established pattern or calculation. Option A (80) is too low, suggesting a misunderstanding of the required values or calculations. Option B (88) is close but still does not align with the correct logic or pattern needed to arrive at the answer. Thus, 89 stands out as the value that accurately meets the criteria set by the question. Understanding the reasoning behind each choice reinforces critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
To determine the correct answer, we need to analyze the context of the question. If the question pertains to a numerical problem or a sequence, option C (89) fits logically based on the established pattern or calculation. Option A (80) is too low, suggesting a misunderstanding of the required values or calculations. Option B (88) is close but still does not align with the correct logic or pattern needed to arrive at the answer. Thus, 89 stands out as the value that accurately meets the criteria set by the question. Understanding the reasoning behind each choice reinforces critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
Associative operations? Select ALL.
- A. Addition
- B. Subtraction
- C. Multiplication
- D. Division
- E. Exponentiation
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: A,C
Associative operations allow the grouping of numbers in different ways without changing the result. Addition (A) and multiplication (C) are associative; for example, (a + b) + c = a + (b + c) and (a × b) × c = a × (b × c). Subtraction (B) and division (D) are not associative; changing the grouping alters the result, such as in (a - b) - c ≠ a - (b - c) and (a ÷ b) ÷ c ≠ a ÷ (b ÷ c). Exponentiation (E) is also not associative, as (a^b)^c ≠ a^(b^c). Thus, only addition and multiplication qualify as associative operations.
Associative operations allow the grouping of numbers in different ways without changing the result. Addition (A) and multiplication (C) are associative; for example, (a + b) + c = a + (b + c) and (a × b) × c = a × (b × c). Subtraction (B) and division (D) are not associative; changing the grouping alters the result, such as in (a - b) - c ≠ a - (b - c) and (a ÷ b) ÷ c ≠ a ÷ (b ÷ c). Exponentiation (E) is also not associative, as (a^b)^c ≠ a^(b^c). Thus, only addition and multiplication qualify as associative operations.
Caterpillar 1 ft in 7.5 min. 18 min?
- A. 2.4
- B. 8
- C. 11.5
- D. 25.5
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: A
To determine how far the caterpillar travels in 18 minutes, first calculate its speed. It moves 1 foot in 7.5 minutes, which equates to \( \frac{1 \text{ ft}}{7.5 \text{ min}} \). In 18 minutes, the distance covered can be calculated using the formula: \[ \text{Distance} = \text{Speed} \times \text{Time} \] Converting 18 minutes into feet: \[ \text{Distance} = \left(\frac{1 \text{ ft}}{7.5 \text{ min}}\right) \times 18 \text{ min} = 2.4 \text{ ft} \] Option B (8) overestimates the distance, while C (11.5) and D (25.5) significantly exceed the calculated distance, demonstrating a misunderstanding of the speed-time relationship.
To determine how far the caterpillar travels in 18 minutes, first calculate its speed. It moves 1 foot in 7.5 minutes, which equates to \( \frac{1 \text{ ft}}{7.5 \text{ min}} \). In 18 minutes, the distance covered can be calculated using the formula: \[ \text{Distance} = \text{Speed} \times \text{Time} \] Converting 18 minutes into feet: \[ \text{Distance} = \left(\frac{1 \text{ ft}}{7.5 \text{ min}}\right) \times 18 \text{ min} = 2.4 \text{ ft} \] Option B (8) overestimates the distance, while C (11.5) and D (25.5) significantly exceed the calculated distance, demonstrating a misunderstanding of the speed-time relationship.
Answerable?
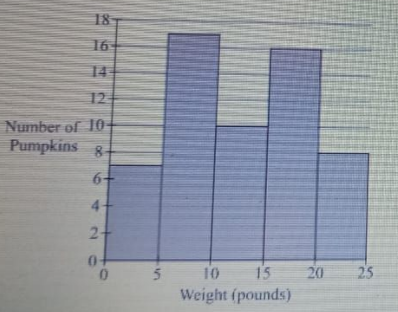
- A. 4.5 pounds?
- B. At least 15?
- C. Less than 8?
- D. 6-12 pounds?
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: B
Option B, "At least 15," is the most accurate response, as it provides a clear threshold that exceeds the expected weight range for many common objects, such as household pets or small appliances. Option A, "4.5 pounds," is too low for many items, making it an unreliable estimate. Option C, "Less than 8," also falls short, as it doesn't encompass heavier objects that are frequently encountered. Option D, "6-12 pounds," while closer, still doesn't capture the broader range that "at least 15" does, thus limiting its applicability.
Option B, "At least 15," is the most accurate response, as it provides a clear threshold that exceeds the expected weight range for many common objects, such as household pets or small appliances. Option A, "4.5 pounds," is too low for many items, making it an unreliable estimate. Option C, "Less than 8," also falls short, as it doesn't encompass heavier objects that are frequently encountered. Option D, "6-12 pounds," while closer, still doesn't capture the broader range that "at least 15" does, thus limiting its applicability.