The great inventor Thomas Edison received more than one thousand patents during his career and made a large contribution to how we live today. For example, in 1877, after discovering a way to record sound, Edison introduced the phonograph. In 1893 he invented the first motion-picture camera. Eight years before inventing the phonograph, Edison received his first patent for a vote recorder, which was intended to help record legislative votes quickly. The Innovation he is most known for is the electric light bulb. He filed a patent for his light bulb in 1879. Though others contributed to the invention of the light bulb, Edison's work made this invention a long-lasting, practical household item.
Which technology mentioned in the passage was the first one invented by Edison?
- A. vote recorder
- B. motion-picture camera
- C. electric light bulb
- D. phonograph
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: A
The vote recorder was the first technology invented by Edison, designed to streamline the voting process. This innovation predates his more famous inventions. The motion-picture camera (B) and electric light bulb (C) came later, showcasing Edison's evolution as an inventor. The phonograph (D), although significant in audio technology, was also developed after the vote recorder. Understanding the chronological order of these inventions highlights Edison's early contributions to technology and their impact on society.
The vote recorder was the first technology invented by Edison, designed to streamline the voting process. This innovation predates his more famous inventions. The motion-picture camera (B) and electric light bulb (C) came later, showcasing Edison's evolution as an inventor. The phonograph (D), although significant in audio technology, was also developed after the vote recorder. Understanding the chronological order of these inventions highlights Edison's early contributions to technology and their impact on society.
Other Related Questions
Complete the U.S. System of Federalism chart based on information from the passage. Click on the title below you want to select and drag it into the top of each column in the chart. - State Government Powers - National Government Powers - Shared Powers of National and State Governments -
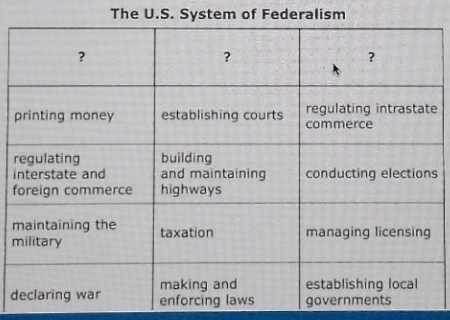
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer:
In the U.S. system of federalism, powers are distributed among different levels of government. **State Government Powers** include authority over education, transportation, and local law enforcement, allowing states to address local needs effectively. **National Government Powers** encompass defense, foreign affairs, and immigration, ensuring a unified national policy in these critical areas. **Shared Powers** involve taxation, infrastructure, and law enforcement, illustrating collaboration between state and national governments to maintain order and promote welfare. Other options may misplace powers or overlook the collaborative nature of federalism, leading to misunderstandings about government functions.
In the U.S. system of federalism, powers are distributed among different levels of government. **State Government Powers** include authority over education, transportation, and local law enforcement, allowing states to address local needs effectively. **National Government Powers** encompass defense, foreign affairs, and immigration, ensuring a unified national policy in these critical areas. **Shared Powers** involve taxation, infrastructure, and law enforcement, illustrating collaboration between state and national governments to maintain order and promote welfare. Other options may misplace powers or overlook the collaborative nature of federalism, leading to misunderstandings about government functions.
How did Chief Justice Marshall contribute to the U.S. government system of checks and balances?
- A. by establishing the Supreme Court's power to check Congress
- B. by creating the power to remove the president from office
- C. by expanding the president's power to check Congress
- D. by giving the Supreme Court the power to control itself
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: A
Chief Justice Marshall played a pivotal role in defining the Supreme Court's authority, notably through the landmark case Marbury v. Madison, which established the principle of judicial review. This empowered the Court to invalidate laws passed by Congress that it deemed unconstitutional, effectively allowing it to check legislative power. Option B is incorrect as the power to remove a president lies with Congress through impeachment, not the Supreme Court. Option C misrepresents Marshall's contributions, as he did not expand presidential power but rather clarified judicial authority. Option D is also inaccurate; the Supreme Court does not have self-regulating powers but operates within the framework of checks and balances.
Chief Justice Marshall played a pivotal role in defining the Supreme Court's authority, notably through the landmark case Marbury v. Madison, which established the principle of judicial review. This empowered the Court to invalidate laws passed by Congress that it deemed unconstitutional, effectively allowing it to check legislative power. Option B is incorrect as the power to remove a president lies with Congress through impeachment, not the Supreme Court. Option C misrepresents Marshall's contributions, as he did not expand presidential power but rather clarified judicial authority. Option D is also inaccurate; the Supreme Court does not have self-regulating powers but operates within the framework of checks and balances.
Which statement is supported by both the table and the map?
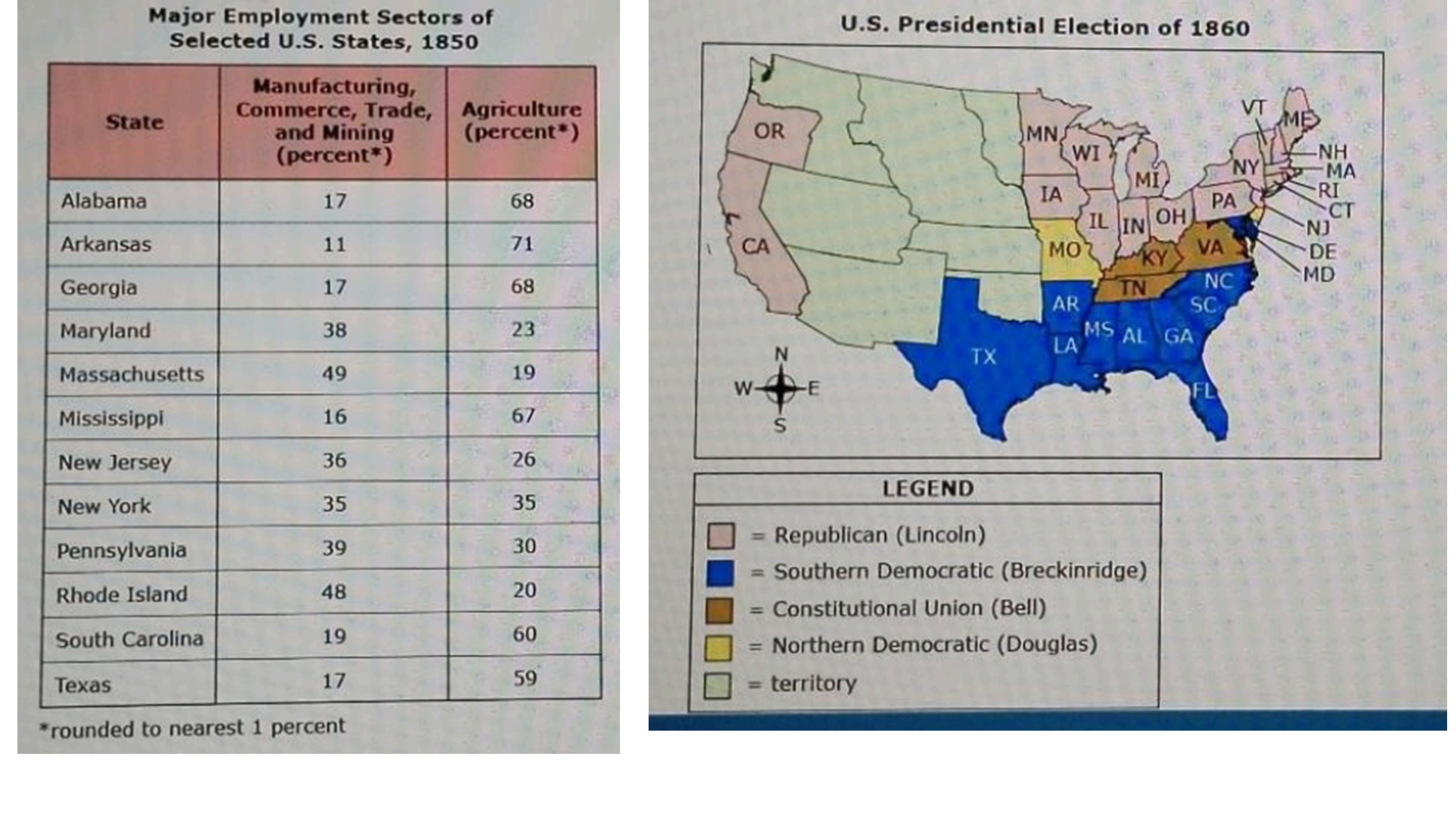
- A. Differences in the total populations of the states led to political differences between the North and the South.
- B. Differences among the economies of the states contributed to political differences between the North and the South.
- C. Political differences between the North and the South reflected differences in education among the states.
- D. Political differences between the North and the South reflected differences in the standards of living in the states.
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: B
Option B is supported by both the table and the map, as they illustrate how varying economic structures—such as agriculture in the South versus industrialization in the North—contributed to distinct political ideologies and policies. Option A incorrectly attributes political differences solely to population size, overlooking the economic factors at play. Option C suggests education differences as the main cause, which is not evident in the provided data. Option D implies that living standards were the primary influence, but the economic context is more directly linked to the political divide. Thus, B effectively encapsulates the relationship between economy and political differences.
Option B is supported by both the table and the map, as they illustrate how varying economic structures—such as agriculture in the South versus industrialization in the North—contributed to distinct political ideologies and policies. Option A incorrectly attributes political differences solely to population size, overlooking the economic factors at play. Option C suggests education differences as the main cause, which is not evident in the provided data. Option D implies that living standards were the primary influence, but the economic context is more directly linked to the political divide. Thus, B effectively encapsulates the relationship between economy and political differences.
How does the message presented by Senator Paul differ from the message presented by President Obama?
- A. Only Senator Paul promotes less government involvement in health care.
- B. Only Senator Paul wants to secure more health care for U.S. citizens.
- C. Only President Obama supports the Supreme Court's right to rule about health care.
- D. Only President Obama discusses problems in the health care industry.
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: A
Senator Paul advocates for reduced government involvement in health care, emphasizing personal choice and market-driven solutions. This contrasts with President Obama's approach, which supports a more active role for the government in expanding access and regulating the industry. Option B is incorrect as both politicians aim to improve health care access, albeit through different methods. Option C misrepresents Obama's stance; he supports health care reforms that align with Supreme Court rulings but does not solely focus on this aspect. Option D is misleading; while Obama addresses health care issues, Senator Paul also discusses industry challenges, making this option inaccurate.
Senator Paul advocates for reduced government involvement in health care, emphasizing personal choice and market-driven solutions. This contrasts with President Obama's approach, which supports a more active role for the government in expanding access and regulating the industry. Option B is incorrect as both politicians aim to improve health care access, albeit through different methods. Option C misrepresents Obama's stance; he supports health care reforms that align with Supreme Court rulings but does not solely focus on this aspect. Option D is misleading; while Obama addresses health care issues, Senator Paul also discusses industry challenges, making this option inaccurate.