This excerpt is from Federalist No. 22, published in 1787. It has been paraphrased.
A legislative rule requiring more than a majority to pass a bill gives the minority more power than the majority. The effect of this practice is the opposite of what is expected in theory. Requiring a unanimous vote or more than a majority vote is meant to provide a safeguard against oppression. But in reality it destroys the thoughtful deliberation of a respectable majority and replaces it with the whims and trickery of a small but unruly gang.
In times of national emergency, the goodness, badness, weakness, and strength of the government is supremely important. The government must in one way or another take action. If a majority resolution can be blocked by a stubborn minority, it will be necessary for the majority to conform to the minority for action to occur. The wishes of the smaller group will override the wishes of the larger group and this will create resentment. In these circumstances, expect constant scheming, trickery, and tiresome delays, resulting in disgraceful deals that violate the public good.
Which quotation from the excerpt reveals the author's bias about the relationship between the rule of the majority and the rights of the minority?
- A. "The wishes of the smaller group will override the wishes of the larger group and this will create resentment."
- B. "Requiring a unanimous vote or more than a majority vote is meant to provide a safeguard against oppression."
- C. "In these circumstances, expect constant scheming, trickery, and tiresome delays, resulting in disgraceful deals that violate the public good."
- D. "In times of national emergency, the goodness, badness, weakness, and strength of the government is supremely important."
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: C
Option C highlights the author's bias by suggesting that the majority's decisions can lead to unethical behavior that undermines public welfare. This reveals a concern for minority rights, indicating that the author believes majority rule may result in negative consequences for those not in power. Option A misrepresents the author's view, as it suggests that the smaller group's wishes will always be overridden, which does not directly reflect bias against majority rule. Option B focuses on safeguards against oppression, which does not convey bias but rather a protective measure. Option D addresses the government's performance during emergencies but fails to connect to the relationship between majority rule and minority rights, missing the core issue of bias.
Option C highlights the author's bias by suggesting that the majority's decisions can lead to unethical behavior that undermines public welfare. This reveals a concern for minority rights, indicating that the author believes majority rule may result in negative consequences for those not in power. Option A misrepresents the author's view, as it suggests that the smaller group's wishes will always be overridden, which does not directly reflect bias against majority rule. Option B focuses on safeguards against oppression, which does not convey bias but rather a protective measure. Option D addresses the government's performance during emergencies but fails to connect to the relationship between majority rule and minority rights, missing the core issue of bias.
Other Related Questions
Which conclusion can be drawn from the diagrams?
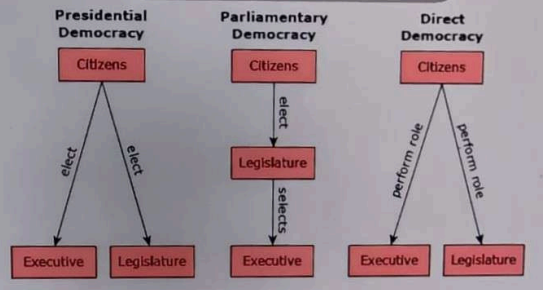
- A. The legislature is more representative of the people in a presidential democracy than in a parliamentary democracy.
- B. The branches of government are more independent of each other in a presidential democracy than in a parliamentary democracy.
- C. The executive branch is more accountable to the people in a parliamentary democracy than in a direct democracy.
- D. The people are more involved in governing in a presidential democracy than in a direct democracy.
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: B
In a presidential democracy, the separation of powers is a key feature, allowing the executive, legislative, and judicial branches to operate independently. This independence enhances checks and balances, ensuring that no single branch can dominate. Option A is incorrect as both systems aim for representation, but the degree can vary based on specific contexts rather than the type of democracy. Option C misrepresents accountability; in parliamentary systems, the executive is directly accountable to the legislature, which is elected by the people. Option D is misleading; in a direct democracy, citizens have direct involvement in governance, often more so than in a presidential system.
In a presidential democracy, the separation of powers is a key feature, allowing the executive, legislative, and judicial branches to operate independently. This independence enhances checks and balances, ensuring that no single branch can dominate. Option A is incorrect as both systems aim for representation, but the degree can vary based on specific contexts rather than the type of democracy. Option C misrepresents accountability; in parliamentary systems, the executive is directly accountable to the legislature, which is elected by the people. Option D is misleading; in a direct democracy, citizens have direct involvement in governance, often more so than in a presidential system.
Based on the excerpt, which change was a result of the National Security Act of 1947?
- A. The Central Intelligence Agency replaced the War Department.
- B. The National Security Council gained control over the Department of Defense.
- C. The Department of Homeland Security replaced the War Department.
- D. The Department of the Navy became part of the Department of Defense.
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: D
The National Security Act of 1947 reorganized the U.S. military and intelligence community. Option D accurately reflects that the Department of the Navy became part of the newly established Department of Defense, streamlining military operations. Option A is incorrect; the CIA was created but did not replace the War Department directly. Option B is misleading; while the National Security Council was established, it does not control the Department of Defense. Option C is factually incorrect, as the Department of Homeland Security was created later, in 2003, not as a result of the 1947 Act.
The National Security Act of 1947 reorganized the U.S. military and intelligence community. Option D accurately reflects that the Department of the Navy became part of the newly established Department of Defense, streamlining military operations. Option A is incorrect; the CIA was created but did not replace the War Department directly. Option B is misleading; while the National Security Council was established, it does not control the Department of Defense. Option C is factually incorrect, as the Department of Homeland Security was created later, in 2003, not as a result of the 1947 Act.
Which one statement identifies the main idea of President Johnson's speech?
- A. The federal government has the responsibility to guarantee the rights of citizens.
- B. The expansion of educational opportunities should be the next goal of the civil rights movement.
- C. The expansion of voting rights can eliminate poverty.
- D. The federal government has power over state governments.
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: A
Option A accurately captures the essence of President Johnson's speech, which emphasizes the government's duty to protect citizens' rights, particularly in the context of civil rights and social justice. Option B, while relevant to the civil rights movement, does not encapsulate the primary focus of the speech, which is broader than just education. Option C suggests a direct correlation between voting rights and poverty alleviation, which, though important, is not the main thrust of Johnson's address. Option D misrepresents the speech's intent, as it does not primarily discuss the federal government's authority over states but rather its role in ensuring citizen rights.
Option A accurately captures the essence of President Johnson's speech, which emphasizes the government's duty to protect citizens' rights, particularly in the context of civil rights and social justice. Option B, while relevant to the civil rights movement, does not encapsulate the primary focus of the speech, which is broader than just education. Option C suggests a direct correlation between voting rights and poverty alleviation, which, though important, is not the main thrust of Johnson's address. Option D misrepresents the speech's intent, as it does not primarily discuss the federal government's authority over states but rather its role in ensuring citizen rights.
Which conclusion is best supported by information in the table and article?
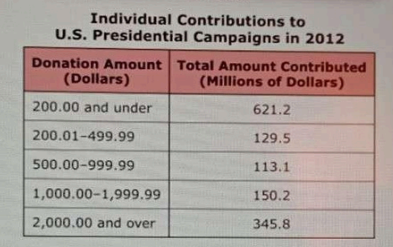
- A. Individuals contributed a total amount of money equal to the total of all other sources of donations.
- B. Individuals contributing the smallest quantity of money insignificantly impact presidential campaigns.
- C. Individuals donated the greatest total amount although many contributions were relatively small.
- D. Individuals have more influence on the proposed policies of presidential candidates than groups do.
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: C
Option C is supported by the data, indicating that while many individual contributions were small, they collectively formed the largest portion of total donations to presidential campaigns. This highlights the significant role individuals play despite the size of their contributions. Option A is incorrect as it suggests individuals’ contributions equaled all other sources, which is not supported by the data. Option B misrepresents the impact of smaller donations; even small contributions can collectively influence campaign funding significantly. Option D overstates individuals' influence on policy compared to groups, which often have more resources and organized lobbying power.
Option C is supported by the data, indicating that while many individual contributions were small, they collectively formed the largest portion of total donations to presidential campaigns. This highlights the significant role individuals play despite the size of their contributions. Option A is incorrect as it suggests individuals’ contributions equaled all other sources, which is not supported by the data. Option B misrepresents the impact of smaller donations; even small contributions can collectively influence campaign funding significantly. Option D overstates individuals' influence on policy compared to groups, which often have more resources and organized lobbying power.