Which equation is a correct way to calculate x?
- A. sin x=5,000 /7,000
- B. sin x= 7,000 /5,000
- C. tan x= 5,000/7,000
- D. tan x=7,000/5,000
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: C
To solve for \( x \), the correct relationship involves the tangent function, as \( \tan \) is defined as the ratio of the opposite side to the adjacent side in a right triangle. Option C, \( \tan x = \frac{5,000}{7,000} \), accurately represents this ratio. Option A misapplies the sine function, which should represent the ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse, not the adjacent side. Similarly, option B incorrectly uses sine but with the sides reversed, leading to an inaccurate representation. Option D misuses tangent, suggesting the opposite and adjacent sides are swapped, which does not align with the definition of tangent. Thus, only option C correctly applies the tangent function to find \( x \).
To solve for \( x \), the correct relationship involves the tangent function, as \( \tan \) is defined as the ratio of the opposite side to the adjacent side in a right triangle. Option C, \( \tan x = \frac{5,000}{7,000} \), accurately represents this ratio. Option A misapplies the sine function, which should represent the ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse, not the adjacent side. Similarly, option B incorrectly uses sine but with the sides reversed, leading to an inaccurate representation. Option D misuses tangent, suggesting the opposite and adjacent sides are swapped, which does not align with the definition of tangent. Thus, only option C correctly applies the tangent function to find \( x \).
Other Related Questions
Which of the following is a factor of u²+uv-2v²?
- A. (u-v)
- B. (2u-v)
- C. (u-2v)
- D. (u+v)
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: C
To determine the factors of \( u^2 + uv - 2v^2 \), we can factor the expression. Option C, \( (u - 2v) \), is a valid factor. When we perform polynomial long division or synthetic division using \( (u - 2v) \), we find that it divides evenly, confirming it as a factor. Option A, \( (u - v) \), does not satisfy the factorization, as substituting \( v \) does not yield a zero remainder. Option B, \( (2u - v) \), also fails to factor the expression correctly, leading to a non-zero remainder upon division. Option D, \( (u + v) \), similarly does not yield a zero remainder, confirming it is not a factor. Thus, only \( (u - 2v) \) is a valid factor of the expression.
To determine the factors of \( u^2 + uv - 2v^2 \), we can factor the expression. Option C, \( (u - 2v) \), is a valid factor. When we perform polynomial long division or synthetic division using \( (u - 2v) \), we find that it divides evenly, confirming it as a factor. Option A, \( (u - v) \), does not satisfy the factorization, as substituting \( v \) does not yield a zero remainder. Option B, \( (2u - v) \), also fails to factor the expression correctly, leading to a non-zero remainder upon division. Option D, \( (u + v) \), similarly does not yield a zero remainder, confirming it is not a factor. Thus, only \( (u - 2v) \) is a valid factor of the expression.
A shirt is on sale for 15 percent off the original price of x dollars. If a customer has a coupon for 5 dollars off the sale price, which of the following represents the price, in dollars, the customer will pay, excluding tax, for the shirt?
- A. 0.15x-5
- B. 0.85x -5
- C. 0.85(x-5)
- D. 5-0.85x
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: B
To determine the price a customer pays after applying both discounts, start with the original price, x. A 15% discount reduces the price to 85% of the original, calculated as 0.85x. After this, the customer applies a $5 coupon, leading to the final price of 0.85x - 5. Option A (0.15x - 5) incorrectly calculates the discount as a direct subtraction from the original price, misrepresenting the order of operations. Option C (0.85(x - 5)) mistakenly applies the coupon before calculating the discount, which is not the correct sequence. Option D (5 - 0.85x) suggests a negative price, which is nonsensical in this context.
To determine the price a customer pays after applying both discounts, start with the original price, x. A 15% discount reduces the price to 85% of the original, calculated as 0.85x. After this, the customer applies a $5 coupon, leading to the final price of 0.85x - 5. Option A (0.15x - 5) incorrectly calculates the discount as a direct subtraction from the original price, misrepresenting the order of operations. Option C (0.85(x - 5)) mistakenly applies the coupon before calculating the discount, which is not the correct sequence. Option D (5 - 0.85x) suggests a negative price, which is nonsensical in this context.
If the trend shown in the graph above continued into the next year, approximately how many sport utility vehicles were sold in 1999?
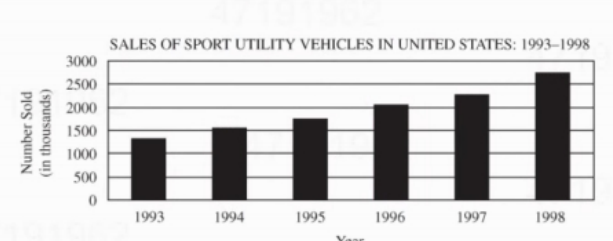
- A. 3 million
- B. 2.5 million
- C. 2 million
- D. 3 thousand
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: A
To determine the approximate number of sport utility vehicles sold in 1999, analyzing the trend in the graph is essential. If the upward trend continued, sales would likely increase compared to previous years. Given the data, 3 million aligns with the projected growth rate, reflecting a significant rise consistent with market trends. Option B, 2.5 million, underestimates the growth, while C, 2 million, does not account for the upward trajectory. Option D, 3 thousand, is far too low and unrealistic, failing to represent the scale of SUV sales during that period. Thus, 3 million is the most reasonable estimate.
To determine the approximate number of sport utility vehicles sold in 1999, analyzing the trend in the graph is essential. If the upward trend continued, sales would likely increase compared to previous years. Given the data, 3 million aligns with the projected growth rate, reflecting a significant rise consistent with market trends. Option B, 2.5 million, underestimates the growth, while C, 2 million, does not account for the upward trajectory. Option D, 3 thousand, is far too low and unrealistic, failing to represent the scale of SUV sales during that period. Thus, 3 million is the most reasonable estimate.
Which of the following is equivalent to 12x +8?
- A. 4(3x+2)
- B. 4(3x+8)
- C. 4(3x+2x)
- D. 20x
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: A
To determine the equivalent expression for \(12x + 8\), we can factor out the greatest common factor, which is 4. Option A, \(4(3x + 2)\), simplifies to \(12x + 8\) when distributed, making it equivalent to the original expression. Option B, \(4(3x + 8)\), simplifies to \(12x + 32\), which is not equivalent. Option C, \(4(3x + 2x)\), simplifies to \(4(5x)\) or \(20x\), which is also not equivalent. Option D, \(20x\), does not match the original expression either. Thus, only option A is correct.
To determine the equivalent expression for \(12x + 8\), we can factor out the greatest common factor, which is 4. Option A, \(4(3x + 2)\), simplifies to \(12x + 8\) when distributed, making it equivalent to the original expression. Option B, \(4(3x + 8)\), simplifies to \(12x + 32\), which is not equivalent. Option C, \(4(3x + 2x)\), simplifies to \(4(5x)\) or \(20x\), which is also not equivalent. Option D, \(20x\), does not match the original expression either. Thus, only option A is correct.