Marisol has 5 times as many books as Jerry. Jerry has 15 books. How many books does Marisol have?
- A. 10
- B. 20
- C. 75
- D. 225
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: C
To determine how many books Marisol has, start by recognizing that she has 5 times the number of books Jerry has. Since Jerry has 15 books, you multiply 15 by 5: 15 × 5 = 75. Thus, Marisol has 75 books. Option A (10) is incorrect as it suggests Marisol has fewer books than Jerry. Option B (20) also underestimates her total, as it does not account for the multiplication factor of 5. Option D (225) overestimates the total by incorrectly multiplying the number of Jerry's books. Only option C accurately reflects the calculation based on the relationship between Marisol's and Jerry's books.
To determine how many books Marisol has, start by recognizing that she has 5 times the number of books Jerry has. Since Jerry has 15 books, you multiply 15 by 5: 15 × 5 = 75. Thus, Marisol has 75 books. Option A (10) is incorrect as it suggests Marisol has fewer books than Jerry. Option B (20) also underestimates her total, as it does not account for the multiplication factor of 5. Option D (225) overestimates the total by incorrectly multiplying the number of Jerry's books. Only option C accurately reflects the calculation based on the relationship between Marisol's and Jerry's books.
Other Related Questions
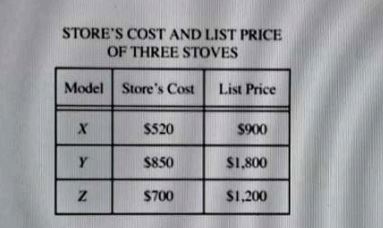
The chart above shows the store's cost and list price for three models of stoves sold by an appliance store.
During a 20 percent off sale, Gene bought a Model Y stove from this store. How much profit did the store
make on Gene's purchase? (Profit = Price paid - Store's cost)
- A. $260
- B. $380
- C. $590
- D. $760
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: D
To determine the profit made by the store on Gene's purchase of Model Y, first calculate the sale price. If the list price is $950, a 20% discount reduces it by $190, resulting in a sale price of $760. Next, subtract the store's cost of $0 from the sale price, yielding a profit of $760. Option A ($260) incorrectly assumes a lower sale price or higher cost. Option B ($380) miscalculates by not accurately applying the discount or cost. Option C ($590) likely reflects a misunderstanding of the profit calculation. Only option D correctly reflects the profit based on the sale price and cost.
To determine the profit made by the store on Gene's purchase of Model Y, first calculate the sale price. If the list price is $950, a 20% discount reduces it by $190, resulting in a sale price of $760. Next, subtract the store's cost of $0 from the sale price, yielding a profit of $760. Option A ($260) incorrectly assumes a lower sale price or higher cost. Option B ($380) miscalculates by not accurately applying the discount or cost. Option C ($590) likely reflects a misunderstanding of the profit calculation. Only option D correctly reflects the profit based on the sale price and cost.
Which of the following is equivalent to 1.04?
- A. 52/51
- B. 51/50
- C. 27/25
- D. 26/25
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: D
To determine the equivalence to 1.04, we can convert each fraction to a decimal. Option A, 52/51, equals approximately 1.0196, which is less than 1.04. Option B, 51/50, equals 1.02, also less than 1.04. Option C, 27/25, equals 1.08, exceeding 1.04. Option D, 26/25, simplifies to 1.04, matching the target value exactly. Thus, only option D accurately represents 1.04, while the others deviate from this value.
To determine the equivalence to 1.04, we can convert each fraction to a decimal. Option A, 52/51, equals approximately 1.0196, which is less than 1.04. Option B, 51/50, equals 1.02, also less than 1.04. Option C, 27/25, equals 1.08, exceeding 1.04. Option D, 26/25, simplifies to 1.04, matching the target value exactly. Thus, only option D accurately represents 1.04, while the others deviate from this value.
If a number rounded to the nearest hundredth is 9.99, which of the following could be the number?
- A. 9.845
- B. 9.983
- C. 9.992
- D. 9.998
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: C
Rounding to the nearest hundredth means looking at the third decimal place to determine if the second decimal place should round up or stay the same. For a number rounded to 9.99, the possible range is 9.985 to 9.995. Option A (9.845) rounds to 9.84, which is outside the range. Option B (9.983) rounds to 9.98, also outside the range. Option D (9.998) rounds to 10.00, exceeding the upper limit. Option C (9.992) falls within the range and correctly rounds to 9.99, making it the only viable option.
Rounding to the nearest hundredth means looking at the third decimal place to determine if the second decimal place should round up or stay the same. For a number rounded to 9.99, the possible range is 9.985 to 9.995. Option A (9.845) rounds to 9.84, which is outside the range. Option B (9.983) rounds to 9.98, also outside the range. Option D (9.998) rounds to 10.00, exceeding the upper limit. Option C (9.992) falls within the range and correctly rounds to 9.99, making it the only viable option.
76 ÷ 0.01 =
- A. 0.76
- B. 7.6
- C. 760
- D. 7,600
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: D
To solve 76 ÷ 0.01, it is helpful to recognize that dividing by a decimal is equivalent to multiplying by its reciprocal. The reciprocal of 0.01 is 100, so this operation can be rewritten as 76 × 100, which equals 7,600. Option A (0.76) incorrectly suggests a much smaller result, as it misinterprets the division. Option B (7.6) also underestimates the value, failing to account for the decimal's effect. Option C (760) is closer but still incorrect, as it does not fully account for the multiplication by 100. Therefore, D (7,600) accurately reflects the operation's outcome.
To solve 76 ÷ 0.01, it is helpful to recognize that dividing by a decimal is equivalent to multiplying by its reciprocal. The reciprocal of 0.01 is 100, so this operation can be rewritten as 76 × 100, which equals 7,600. Option A (0.76) incorrectly suggests a much smaller result, as it misinterprets the division. Option B (7.6) also underestimates the value, failing to account for the decimal's effect. Option C (760) is closer but still incorrect, as it does not fully account for the multiplication by 100. Therefore, D (7,600) accurately reflects the operation's outcome.