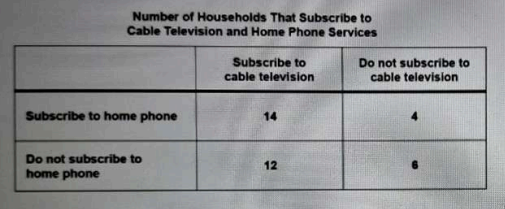
Malia collected information about whether the members of the 36 households on her block subscribed to cable television and home phone services. Her results are shown in the table below.\nIf a household on Malia's block is selected at random and does subscribe to cable television, what is the probability the members of the household also subscribe to home phone service?
- A. 14/18
- B. 14/26
- C. 18/36
- D. 14/36
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: A
To determine the probability that a household subscribes to home phone service given that it subscribes to cable television, we focus on the relevant subset of households. Malia found 18 households that subscribe to cable, out of which 14 also subscribe to home phone service. Thus, the probability is calculated as the number of households with both services (14) divided by the total number of households with cable (18), resulting in 14/18. Option B (14/26) incorrectly uses the total number of households with home phone service instead of just those with cable. Option C (18/36) misinterprets the probability as a ratio of all households rather than those who subscribe to cable. Option D (14/36) inaccurately represents the total number of households instead of focusing on the cable subscribers.
To determine the probability that a household subscribes to home phone service given that it subscribes to cable television, we focus on the relevant subset of households. Malia found 18 households that subscribe to cable, out of which 14 also subscribe to home phone service. Thus, the probability is calculated as the number of households with both services (14) divided by the total number of households with cable (18), resulting in 14/18. Option B (14/26) incorrectly uses the total number of households with home phone service instead of just those with cable. Option C (18/36) misinterprets the probability as a ratio of all households rather than those who subscribe to cable. Option D (14/36) inaccurately represents the total number of households instead of focusing on the cable subscribers.
Other Related Questions
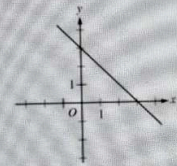
Which of the following could be an equation of the line graphed in the xy-plane above?
- A. y=-x-3
- B. y=-x+3
- C. y=x-3
- D. y=x+3
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: D
To determine the equation of the line, we analyze its slope and y-intercept. The line in the graph has a positive slope, indicating that as \(x\) increases, \(y\) also increases. Option D, \(y = x + 3\), has a positive slope of 1 and a y-intercept of 3, aligning with the graph's characteristics. Option A, \(y = -x - 3\), has a negative slope and would decrease as \(x\) increases, which contradicts the graph. Option B, \(y = -x + 3\), also has a negative slope, leading to a downward trend. Option C, \(y = x - 3\), has a positive slope but a y-intercept of -3, placing it below the graph. Thus, D is the only option that fits the observed line.
To determine the equation of the line, we analyze its slope and y-intercept. The line in the graph has a positive slope, indicating that as \(x\) increases, \(y\) also increases. Option D, \(y = x + 3\), has a positive slope of 1 and a y-intercept of 3, aligning with the graph's characteristics. Option A, \(y = -x - 3\), has a negative slope and would decrease as \(x\) increases, which contradicts the graph. Option B, \(y = -x + 3\), also has a negative slope, leading to a downward trend. Option C, \(y = x - 3\), has a positive slope but a y-intercept of -3, placing it below the graph. Thus, D is the only option that fits the observed line.
0.034÷(10)^(-1) =
- A. 0.0034
- B. 0.034
- C. 0.34
- D. 3.4
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: C
To solve 0.034 ÷ (10)^(-1), we first recognize that (10)^(-1) is equivalent to 1/10 or 0.1. Dividing by 0.1 is the same as multiplying by 10. Therefore, 0.034 ÷ 0.1 equals 0.034 × 10, which results in 0.34. Option A (0.0034) misinterprets the division, mistakenly moving the decimal too far left. Option B (0.034) fails to account for the division by 0.1, leaving the original number unchanged. Option D (3.4) incorrectly multiplies instead of dividing, moving the decimal point too far right. Thus, the only accurate calculation leads to 0.34.
To solve 0.034 ÷ (10)^(-1), we first recognize that (10)^(-1) is equivalent to 1/10 or 0.1. Dividing by 0.1 is the same as multiplying by 10. Therefore, 0.034 ÷ 0.1 equals 0.034 × 10, which results in 0.34. Option A (0.0034) misinterprets the division, mistakenly moving the decimal too far left. Option B (0.034) fails to account for the division by 0.1, leaving the original number unchanged. Option D (3.4) incorrectly multiplies instead of dividing, moving the decimal point too far right. Thus, the only accurate calculation leads to 0.34.
3√2- 2/(√2) =
- A. 2√2
- B. √2
- C. 3
- D. 4
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: A
To solve the expression \( 3\sqrt{2} - \frac{2}{\sqrt{2}} \), we first simplify \( \frac{2}{\sqrt{2}} \). This can be rewritten as \( \frac{2\sqrt{2}}{2} = \sqrt{2} \). Thus, the expression becomes \( 3\sqrt{2} - \sqrt{2} \), which simplifies to \( 2\sqrt{2} \). Option B (\( \sqrt{2} \)) is incorrect as it does not account for the subtraction from \( 3\sqrt{2} \). Option C (3) is incorrect because it misrepresents the value obtained after simplification. Option D (4) is also incorrect, as it does not relate to the expression at all.
To solve the expression \( 3\sqrt{2} - \frac{2}{\sqrt{2}} \), we first simplify \( \frac{2}{\sqrt{2}} \). This can be rewritten as \( \frac{2\sqrt{2}}{2} = \sqrt{2} \). Thus, the expression becomes \( 3\sqrt{2} - \sqrt{2} \), which simplifies to \( 2\sqrt{2} \). Option B (\( \sqrt{2} \)) is incorrect as it does not account for the subtraction from \( 3\sqrt{2} \). Option C (3) is incorrect because it misrepresents the value obtained after simplification. Option D (4) is also incorrect, as it does not relate to the expression at all.
Trevani bought a book. She paid a total of $13.50, including 8% sales tax. How much tax did Trevani pay on the book?
- A. $0.96
- B. $1.00
- C. $1.04
- D. $1.08
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: B
To find the amount of sales tax Trevani paid, first determine the price before tax. The total amount paid, $13.50, includes an 8% tax. To find the pre-tax amount, divide the total by 1.08 (which accounts for the original price plus tax): $13.50 ÷ 1.08 = $12.50. Next, calculate the sales tax by subtracting the pre-tax amount from the total: $13.50 - $12.50 = $1.00. This confirms that Trevani paid $1.00 in tax. - Option A ($0.96) is incorrect as it underestimates the tax. - Option C ($1.04) slightly overestimates the tax. - Option D ($1.08) incorrectly assumes the total is all tax without accounting for the book's price.
To find the amount of sales tax Trevani paid, first determine the price before tax. The total amount paid, $13.50, includes an 8% tax. To find the pre-tax amount, divide the total by 1.08 (which accounts for the original price plus tax): $13.50 ÷ 1.08 = $12.50. Next, calculate the sales tax by subtracting the pre-tax amount from the total: $13.50 - $12.50 = $1.00. This confirms that Trevani paid $1.00 in tax. - Option A ($0.96) is incorrect as it underestimates the tax. - Option C ($1.04) slightly overestimates the tax. - Option D ($1.08) incorrectly assumes the total is all tax without accounting for the book's price.