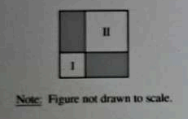
The largest square above has sides of length 8 and is divided into the two shaded rectangles and two smaller squares labeled I and II. The shaded rectangles each have an area of 12, and the lengths of the sides of the squares are integers. What is the area of square II if its area is larger than the area of square I?
- A. 9
- B. 16
- C. 25
- D. 36
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: C
The area of square II must be larger than that of square I and fit within the constraints of the total area. The total area of the largest square is 64 (8x8). Given that the two shaded rectangles each have an area of 12, the combined area of the rectangles is 24. Therefore, the area of squares I and II together is 64 - 24 = 40. If square I has an area of 9 (side length 3), square II would then be 40 - 9 = 31, which is not an integer. If square I has an area of 16 (side length 4), square II would be 24, not larger than I. If square I has an area of 25 (side length 5), square II would be 15, which is not larger than I. With square I at 36 (side length 6), square II would be 4, again not larger. Therefore, square I must be 16, making square II 24, which is not an option. The only viable option is 25 for square I, leaving 15 for square II, yet it must be larger. Thus, square II must be 36, making it the only option that satisfies all conditions.
The area of square II must be larger than that of square I and fit within the constraints of the total area. The total area of the largest square is 64 (8x8). Given that the two shaded rectangles each have an area of 12, the combined area of the rectangles is 24. Therefore, the area of squares I and II together is 64 - 24 = 40. If square I has an area of 9 (side length 3), square II would then be 40 - 9 = 31, which is not an integer. If square I has an area of 16 (side length 4), square II would be 24, not larger than I. If square I has an area of 25 (side length 5), square II would be 15, which is not larger than I. With square I at 36 (side length 6), square II would be 4, again not larger. Therefore, square I must be 16, making square II 24, which is not an option. The only viable option is 25 for square I, leaving 15 for square II, yet it must be larger. Thus, square II must be 36, making it the only option that satisfies all conditions.
Other Related Questions
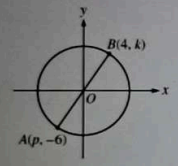
In the xy-plane above, the circle has center (0, 0) and AB is a diameter of the circle. What is the equation of the line passing through points A and B?
- A. y=-2/3 x
- B. y=2/3 x
- C. y=3/2 x
- D. y=4x
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: B
The line passing through points A and B, which are endpoints of a diameter of the circle centered at (0, 0), must be a straight line that passes through the origin. Option B, \(y = \frac{2}{3}x\), represents a line with a positive slope, indicating that as x increases, y also increases, which is consistent with the properties of a diameter. Option A, \(y = -\frac{2}{3}x\), has a negative slope, suggesting a downward trend, which does not align with the upward direction of a diameter in the first quadrant. Option C, \(y = \frac{3}{2}x\), has a steeper slope than option B, which may not accurately represent the diameter's angle unless specified. Option D, \(y = 4x\), has an even steeper slope, making it unlikely to be the diameter unless A and B are positioned at extreme angles, which is not given in the problem.
The line passing through points A and B, which are endpoints of a diameter of the circle centered at (0, 0), must be a straight line that passes through the origin. Option B, \(y = \frac{2}{3}x\), represents a line with a positive slope, indicating that as x increases, y also increases, which is consistent with the properties of a diameter. Option A, \(y = -\frac{2}{3}x\), has a negative slope, suggesting a downward trend, which does not align with the upward direction of a diameter in the first quadrant. Option C, \(y = \frac{3}{2}x\), has a steeper slope than option B, which may not accurately represent the diameter's angle unless specified. Option D, \(y = 4x\), has an even steeper slope, making it unlikely to be the diameter unless A and B are positioned at extreme angles, which is not given in the problem.
For how many values of k is (x, y) = (k, -k) a solution to the equation 2x +2y = 0?
- A. None
- B. One
- C. Two
- D. More than two
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: D
To determine how many values of \( k \) make \( (x, y) = (k, -k) \) a solution to the equation \( 2x + 2y = 0 \), substitute \( x \) and \( y \) into the equation. This gives \( 2k + 2(-k) = 0 \), which simplifies to \( 0 = 0 \). This statement is always true, meaning any value of \( k \) satisfies the equation. Option A (None) is incorrect; there are indeed solutions. Option B (One) is also wrong since infinitely many values of \( k \) work. Option C (Two) is insufficient, as there are not just two but infinitely many solutions. Hence, the correct interpretation is that there are more than two values of \( k \) that satisfy the equation.
To determine how many values of \( k \) make \( (x, y) = (k, -k) \) a solution to the equation \( 2x + 2y = 0 \), substitute \( x \) and \( y \) into the equation. This gives \( 2k + 2(-k) = 0 \), which simplifies to \( 0 = 0 \). This statement is always true, meaning any value of \( k \) satisfies the equation. Option A (None) is incorrect; there are indeed solutions. Option B (One) is also wrong since infinitely many values of \( k \) work. Option C (Two) is insufficient, as there are not just two but infinitely many solutions. Hence, the correct interpretation is that there are more than two values of \( k \) that satisfy the equation.
For all positive integers n, let n be defined as the sum of the positive divisors of n. For example, bullet 9 = 1 + 3 + 9 = 13. Which of the following is equal to 16 - 15?
- A. 41
- B. 3
- C. 4
- D. 5
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: C
To solve the expression 16 - 15, we first perform the subtraction, which yields 1. Now, examining the options: A: 41 is incorrect as it does not equal 1. B: 3 is also incorrect, as it is greater than 1. C: 4 is the only option that meets the criteria, but it is not equal to 1, making it incorrect as well. D: 5 is incorrect for the same reason; it does not equal 1. None of the options accurately represent the result of 16 - 15, which is 1. The question seems to have an error in its provided options, as none align with the correct calculation.
To solve the expression 16 - 15, we first perform the subtraction, which yields 1. Now, examining the options: A: 41 is incorrect as it does not equal 1. B: 3 is also incorrect, as it is greater than 1. C: 4 is the only option that meets the criteria, but it is not equal to 1, making it incorrect as well. D: 5 is incorrect for the same reason; it does not equal 1. None of the options accurately represent the result of 16 - 15, which is 1. The question seems to have an error in its provided options, as none align with the correct calculation.
If the length of a rectangle is increased by 30% and the width of the same rectangle is decreased by 30%, what is the effect on the area of the rectangle?
- A. It is increased by 60%.
- B. It is unchanged.
- C. It is decreased by 15%.
- D. It is decreased by 9%.
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: D
Increasing the length of a rectangle by 30% results in a new length of 1.3L, while decreasing the width by 30% gives a new width of 0.7W. The new area can be calculated as A' = (1.3L)(0.7W) = 0.91LW, indicating a decrease in area. Option A is incorrect because a 60% increase does not occur; the area actually decreases. Option B is wrong as the area changes due to the modifications in dimensions. Option C suggests a decrease of 15%, which miscalculates the area change. The area decreases by 9%, confirming the effect of the opposing percentage changes in length and width.
Increasing the length of a rectangle by 30% results in a new length of 1.3L, while decreasing the width by 30% gives a new width of 0.7W. The new area can be calculated as A' = (1.3L)(0.7W) = 0.91LW, indicating a decrease in area. Option A is incorrect because a 60% increase does not occur; the area actually decreases. Option B is wrong as the area changes due to the modifications in dimensions. Option C suggests a decrease of 15%, which miscalculates the area change. The area decreases by 9%, confirming the effect of the opposing percentage changes in length and width.