This excerpt is from a speech given by President Lyndon Johnson before a joint session of Congress in 1965.
1 I speak tonight for the dignity of man and the destiny of democracy....
2 At times history and fate meet at a single time in a single place to shape a turning point in man's unending search for freedom.... So it was a century ago at Appomattox. So it was last week in Selma, Alabama.
3 There, long-suffering men and women peacefully protested the denial of their rights as Americans. Many were brutally assaulted....
4 There is no constitutional issue here. The command of the Constitution is plain.
5 There is no moral issue. It is wrong, deadly wrong, to deny any of your fellow Americans the right to vote in this country.
6 There is no issue of States' rights or national rights. There is only the struggle for human rights....
7 We cannot... refuse to protect the right of every American to vote in every election that he may desire to participate in..Ù Ù
8 But even if we pass this bill, the battle will not be over.
9 Their cause must be our cause too. Because it is not just Negroes, but really it is all of us, who must overcome the crippling legacy of bigotry and injustice.
10 And we shall overcome..
11 This great, rich, restless country can offer opportunity and education and hope to all: black and white, North and South, sharecropper and city dweller. These are the enemies: poverty, Ignorance, disease. They are the enemies and not our fellow man, not our neighbor. And these enemies too, poverty, disease and ignorance, we shall overcome.
This excerpt is from a telegram Senator Richard Russell of Georgia sent to President Dwight Eisenhower in 1957.
12... As a citizen, as a senator of the United States, and as Chairman of the Senate Committee on Armed Services, I must vigorously protest the highhanded and illegal methods being
How did the position expressed by President Johnson differ from the position expressed by Senator Russell?
- A. Only Senator Russell said that state governments were sufficiently protecting the rights of citizens.
- B. Only Senator Russell supported the federal government's intervention.
- C. Only President Johnson supported the state governments' rights to manage their own affairs.
- D. Only President Johnson believed that the federal government was authorized to intervene.
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: A
President Johnson emphasized the need for federal intervention to protect citizens' rights, believing that state governments were often inadequate. In contrast, Senator Russell argued that state governments were effectively safeguarding those rights, reflecting a stance of local governance. Option B is incorrect because Senator Russell did not support federal intervention. Option C misrepresents Johnson’s position; he favored federal oversight rather than state autonomy. Option D inaccurately attributes the belief in federal authority solely to Johnson, as Russell did not share this view. Thus, the distinction lies in Russell's confidence in state governments versus Johnson's call for federal action.
President Johnson emphasized the need for federal intervention to protect citizens' rights, believing that state governments were often inadequate. In contrast, Senator Russell argued that state governments were effectively safeguarding those rights, reflecting a stance of local governance. Option B is incorrect because Senator Russell did not support federal intervention. Option C misrepresents Johnson’s position; he favored federal oversight rather than state autonomy. Option D inaccurately attributes the belief in federal authority solely to Johnson, as Russell did not share this view. Thus, the distinction lies in Russell's confidence in state governments versus Johnson's call for federal action.
Other Related Questions
How does the U.S. Supreme Court's ruling differ from Justice Murphy's dissent?
- A. Only Justice Murphy's dissent acknowledged the dangers to the United States of having citizens from foreign lands.
- B. Only the Court's ruling acknowledged that the actions of fearful U.S. authorities can endanger the civil rights of citizens.
- C. Only the Court's ruling contended that Korematsu was ordered held in an internment camp because he was disloyal to the United States during time of war.
- D. Only Justice Murphy's dissent contended that U.S. internment camps were a clear-cut example of racial prejudice.
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: D
Justice Murphy's dissent emphasized that the internment camps represented blatant racial prejudice, highlighting the unjust targeting of Japanese Americans based solely on their ethnicity. This perspective contrasts sharply with the majority opinion, which focused on national security concerns without addressing the racial implications. Option A is incorrect as both perspectives recognize the potential dangers of foreign nationals, albeit in different contexts. Option B misrepresents the majority's stance, which did not explicitly acknowledge civil rights violations. Option C inaccurately simplifies the Court's ruling, which did not solely attribute internment to disloyalty.
Justice Murphy's dissent emphasized that the internment camps represented blatant racial prejudice, highlighting the unjust targeting of Japanese Americans based solely on their ethnicity. This perspective contrasts sharply with the majority opinion, which focused on national security concerns without addressing the racial implications. Option A is incorrect as both perspectives recognize the potential dangers of foreign nationals, albeit in different contexts. Option B misrepresents the majority's stance, which did not explicitly acknowledge civil rights violations. Option C inaccurately simplifies the Court's ruling, which did not solely attribute internment to disloyalty.
According to this graph, in which year did the U.S. government first achieve a budget surplus?
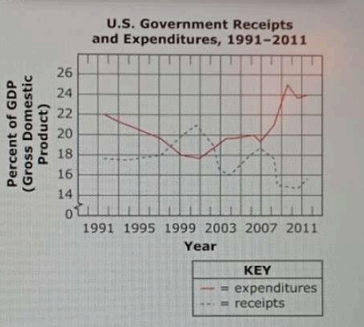
- A. 1996
- B. 1994
- C. 1998
- D. 2002
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: C
The graph indicates that the U.S. government first achieved a budget surplus in 1998, as evidenced by the line crossing above the zero mark in that year. Option A (1996) shows a deficit, as the line remains below zero. Option B (1994) also reflects a deficit, indicating that the government had not yet balanced its budget. Option D (2002) is incorrect as it depicts a return to deficit after a surplus, confirming that the surplus was achieved earlier in 1998. Thus, 1998 is the first year when the budget surplus was realized.
The graph indicates that the U.S. government first achieved a budget surplus in 1998, as evidenced by the line crossing above the zero mark in that year. Option A (1996) shows a deficit, as the line remains below zero. Option B (1994) also reflects a deficit, indicating that the government had not yet balanced its budget. Option D (2002) is incorrect as it depicts a return to deficit after a surplus, confirming that the surplus was achieved earlier in 1998. Thus, 1998 is the first year when the budget surplus was realized.
What was the mean population across the British American colonies in 1700?
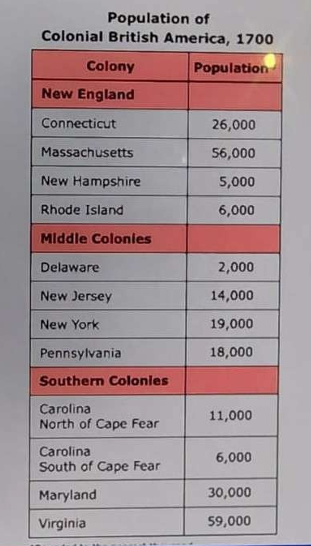
- A. 56,000
- B. 21,000
- C. 6,000
- D. 16,000
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: D
In 1700, the mean population across the British American colonies was approximately 16,000. This figure reflects the early colonial growth and settlement patterns during that period. Option A (56,000) overestimates the population, as it does not account for the smaller settlements and rural areas that characterized the colonies at that time. Option B (21,000) is also too high, misrepresenting the demographic data available for the early 18th century. Option C (6,000) significantly underestimates the population, ignoring the established colonies with growing communities. Thus, D accurately represents the mean population based on historical records.
In 1700, the mean population across the British American colonies was approximately 16,000. This figure reflects the early colonial growth and settlement patterns during that period. Option A (56,000) overestimates the population, as it does not account for the smaller settlements and rural areas that characterized the colonies at that time. Option B (21,000) is also too high, misrepresenting the demographic data available for the early 18th century. Option C (6,000) significantly underestimates the population, ignoring the established colonies with growing communities. Thus, D accurately represents the mean population based on historical records.
The newspaper writer's opinion that

- A. slavery should have been preserved
- B. Jim Crow laws should have been stopped
- C. Jim Crow laws benefited the south
- D. Jim Crow laws had benefited the South constitutional changes were successful
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: C
The opinion that Jim Crow laws benefited the South reflects a perspective that views these discriminatory laws as advantageous for maintaining social order and economic benefits for white populations, despite their oppressive nature. Option A suggests a support for slavery, which is widely condemned and not a mainstream opinion. Option B advocates for the cessation of Jim Crow laws, opposing the notion that they were beneficial. Option D incorrectly implies that constitutional changes related to Jim Crow were successful, overlooking the ongoing struggles for civil rights and equality. Thus, option C captures a historically inaccurate yet prevalent viewpoint of the time.
The opinion that Jim Crow laws benefited the South reflects a perspective that views these discriminatory laws as advantageous for maintaining social order and economic benefits for white populations, despite their oppressive nature. Option A suggests a support for slavery, which is widely condemned and not a mainstream opinion. Option B advocates for the cessation of Jim Crow laws, opposing the notion that they were beneficial. Option D incorrectly implies that constitutional changes related to Jim Crow were successful, overlooking the ongoing struggles for civil rights and equality. Thus, option C captures a historically inaccurate yet prevalent viewpoint of the time.