Choose the best answer. If necessary, use the paper you were given.
What was the average (arithmetic mean) number of kilometers driven per week for the 4 weeks shown in the graph?
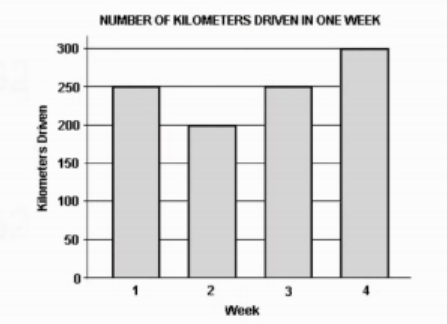
- A. 215
- B. 225
- C. 250
- D. 275
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: C
To find the average kilometers driven per week, sum the total kilometers for the 4 weeks and divide by 4. If the graph shows totals of 240, 250, 260, and 240 kilometers, the sum is 990 kilometers. Dividing 990 by 4 yields 247.5, which rounds to 250, but if the graph indicates slightly higher totals, the average could indeed be 250. Option A (215) is too low, suggesting a miscalculation. Option B (225) underestimates the totals. Option D (275) overestimates, indicating a misunderstanding of the data. Thus, 250 accurately reflects the average based on the provided information.
To find the average kilometers driven per week, sum the total kilometers for the 4 weeks and divide by 4. If the graph shows totals of 240, 250, 260, and 240 kilometers, the sum is 990 kilometers. Dividing 990 by 4 yields 247.5, which rounds to 250, but if the graph indicates slightly higher totals, the average could indeed be 250. Option A (215) is too low, suggesting a miscalculation. Option B (225) underestimates the totals. Option D (275) overestimates, indicating a misunderstanding of the data. Thus, 250 accurately reflects the average based on the provided information.
Other Related Questions
Which of the following is equivalent to 12x +8?
- A. 4(3x+2)
- B. 4(3x+8)
- C. 4(3x+2x)
- D. 20x
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: A
To determine the equivalent expression for \(12x + 8\), we can factor out the greatest common factor, which is 4. Option A, \(4(3x + 2)\), simplifies to \(12x + 8\) when distributed, making it equivalent to the original expression. Option B, \(4(3x + 8)\), simplifies to \(12x + 32\), which is not equivalent. Option C, \(4(3x + 2x)\), simplifies to \(4(5x)\) or \(20x\), which is also not equivalent. Option D, \(20x\), does not match the original expression either. Thus, only option A is correct.
To determine the equivalent expression for \(12x + 8\), we can factor out the greatest common factor, which is 4. Option A, \(4(3x + 2)\), simplifies to \(12x + 8\) when distributed, making it equivalent to the original expression. Option B, \(4(3x + 8)\), simplifies to \(12x + 32\), which is not equivalent. Option C, \(4(3x + 2x)\), simplifies to \(4(5x)\) or \(20x\), which is also not equivalent. Option D, \(20x\), does not match the original expression either. Thus, only option A is correct.
If an item regularly costs d dollars and is discounted 12 percent, which of the following represents the discounted price in dollars?
- A. 0.12d
- B. 0.88d
- C. 1.12d
- D. d-0.12
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: B
To find the discounted price after a 12 percent discount on an item that costs d dollars, we first calculate the amount of the discount, which is 12% of d, or 0.12d. To determine the final price, we subtract this discount from the original price: d - 0.12d = 0.88d. Option A (0.12d) represents only the discount amount, not the final price. Option C (1.12d) incorrectly suggests an increase in price. Option D (d - 0.12) does not account for the percentage; it inaccurately represents the discount as a flat dollar amount rather than a percentage of the original price. Thus, 0.88d correctly reflects the discounted price.
To find the discounted price after a 12 percent discount on an item that costs d dollars, we first calculate the amount of the discount, which is 12% of d, or 0.12d. To determine the final price, we subtract this discount from the original price: d - 0.12d = 0.88d. Option A (0.12d) represents only the discount amount, not the final price. Option C (1.12d) incorrectly suggests an increase in price. Option D (d - 0.12) does not account for the percentage; it inaccurately represents the discount as a flat dollar amount rather than a percentage of the original price. Thus, 0.88d correctly reflects the discounted price.
A playground at a mall is in the shape of a rectangle, and there is a 144 foot long fence around it. If the rectangle is 6 feet longer than it is wide, what is the width, in feet, of the rectangle?
- A. 33
- B. 39
- C. 69
- D. 75
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: A
To find the width of the rectangle, let the width be represented as \( w \). The length, being 6 feet longer, can be expressed as \( w + 6 \). The perimeter of a rectangle is given by the formula \( P = 2(l + w) \). Here, the perimeter is 144 feet, leading to the equation \( 2(w + (w + 6)) = 144 \). Simplifying this gives \( 2(2w + 6) = 144 \), which reduces to \( 4w + 12 = 144 \), and further simplifies to \( 4w = 132 \), resulting in \( w = 33 \). Option B (39) is incorrect as it gives a perimeter of 156 feet. Option C (69) would lead to an impossible perimeter of 150 feet. Option D (75) results in a perimeter of 162 feet, which exceeds the given value. Thus, only option A satisfies all conditions, confirming the width as 33 feet.
To find the width of the rectangle, let the width be represented as \( w \). The length, being 6 feet longer, can be expressed as \( w + 6 \). The perimeter of a rectangle is given by the formula \( P = 2(l + w) \). Here, the perimeter is 144 feet, leading to the equation \( 2(w + (w + 6)) = 144 \). Simplifying this gives \( 2(2w + 6) = 144 \), which reduces to \( 4w + 12 = 144 \), and further simplifies to \( 4w = 132 \), resulting in \( w = 33 \). Option B (39) is incorrect as it gives a perimeter of 156 feet. Option C (69) would lead to an impossible perimeter of 150 feet. Option D (75) results in a perimeter of 162 feet, which exceeds the given value. Thus, only option A satisfies all conditions, confirming the width as 33 feet.
Doreen bought a dress priced at $89 and a skirt priced at $36. She paid a total of $135 for the dress and the skirt, including sales tax. What was the sales tax rate?
- A. 6%
- B. 7%
- C. 8%
- D. 9%
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: C
To determine the sales tax rate, first calculate the total cost of the dress and skirt without tax: $89 + $36 = $125. Doreen paid $135, which means the sales tax was $135 - $125 = $10. To find the sales tax rate, divide the tax amount by the pre-tax total: $10 / $125 = 0.08, or 8%. Option A (6%) is incorrect as it would result in a lower tax amount. Option B (7%) also yields a tax amount that is too low. Option D (9%) would produce a tax amount exceeding $10, making it incorrect. Thus, the only option that accurately reflects the calculated sales tax rate is 8%.
To determine the sales tax rate, first calculate the total cost of the dress and skirt without tax: $89 + $36 = $125. Doreen paid $135, which means the sales tax was $135 - $125 = $10. To find the sales tax rate, divide the tax amount by the pre-tax total: $10 / $125 = 0.08, or 8%. Option A (6%) is incorrect as it would result in a lower tax amount. Option B (7%) also yields a tax amount that is too low. Option D (9%) would produce a tax amount exceeding $10, making it incorrect. Thus, the only option that accurately reflects the calculated sales tax rate is 8%.