This passage discusses the first national government in the United States.
In 1781, the 13 former British American colonies established a common government when they ratified the Articles of Confederation. The document established a "firm league of friendship" between the states and reserved the greatest share of political authority to the individual states. The new confederation had only one branch, which was made up of a one-house legislature in which the states were equally represented. Among other powers, the new government had the power to conduct foreign affairs for the 13 independent states. It had the power to make war and peace and to negotiate treaties with foreign countries. It could also settle disputes between the states, Including disputes over western territories. Each of the states retained their "sovereignty, freedom and independence." Under the Articles, Congress could not collect taxes, regulate trade between states, or enforce laws. The confederation was replaced in 1787 by the government created by the U.S. Constitution.
What is the meaning of confederation in this passage?
- A. a government in which the whole population of a country votes to make laws for the people
- B. a political union in which power is divided between a strong central authority and the various other political units
- C. a political union in which the component units retain significant independence from the central government
- D. a government in which people vote to elect representatives who make laws for the people
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: C
Confederation refers to a political union where individual components maintain considerable autonomy while cooperating for mutual benefit. Option C accurately captures this definition, emphasizing the independence of component units from the central authority. Option A describes a direct democracy, which is not aligned with the concept of confederation. Option B suggests a balance of power that leans towards a strong central authority, contradicting the essence of a confederation. Option D outlines a representative democracy, which does not inherently involve the independence of component units, thus misrepresenting the nature of a confederation.
Confederation refers to a political union where individual components maintain considerable autonomy while cooperating for mutual benefit. Option C accurately captures this definition, emphasizing the independence of component units from the central authority. Option A describes a direct democracy, which is not aligned with the concept of confederation. Option B suggests a balance of power that leans towards a strong central authority, contradicting the essence of a confederation. Option D outlines a representative democracy, which does not inherently involve the independence of component units, thus misrepresenting the nature of a confederation.
Other Related Questions
Which technology mentioned in the passage was the first one invented by Edison?
- A. vote recorder
- B. motion-picture camera
- C. electric light bulb
- D. phonograph
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: A
The vote recorder was the first technology invented by Edison, designed to streamline the voting process. This innovation predates his more famous inventions. The motion-picture camera (B) and electric light bulb (C) came later, showcasing Edison's evolution as an inventor. The phonograph (D), although significant in audio technology, was also developed after the vote recorder. Understanding the chronological order of these inventions highlights Edison's early contributions to technology and their impact on society.
The vote recorder was the first technology invented by Edison, designed to streamline the voting process. This innovation predates his more famous inventions. The motion-picture camera (B) and electric light bulb (C) came later, showcasing Edison's evolution as an inventor. The phonograph (D), although significant in audio technology, was also developed after the vote recorder. Understanding the chronological order of these inventions highlights Edison's early contributions to technology and their impact on society.
The United States fought in World War II from 1941 to 1945. Which statement explains the peak annual inflation rate during the 1940s?
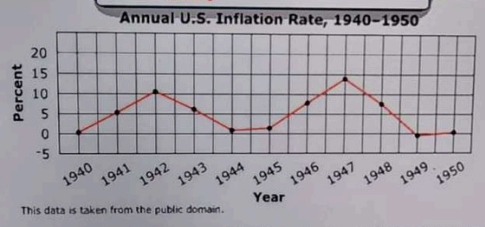
- A. Consumer demand increased due to the end of rationing.
- B. Manufacturing decreased because of less demand for weapons.
- C. Government spending increased due to national defense.
- D. Wages decreased because of competition for scarce jobs.
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: C
The peak annual inflation rate during the 1940s can be attributed to increased government spending due to national defense efforts. This surge in spending stimulated the economy and raised prices as the demand for goods and services outpaced supply. Option A is incorrect; while consumer demand did rise post-rationing, it was not the primary driver of inflation during the war years. Option B is also wrong, as manufacturing actually increased during the war to meet military needs. Option D misrepresents the labor market; wages generally rose due to high demand for workers, not decreased. Thus, government spending for defense was the key factor in driving inflation during this period.
The peak annual inflation rate during the 1940s can be attributed to increased government spending due to national defense efforts. This surge in spending stimulated the economy and raised prices as the demand for goods and services outpaced supply. Option A is incorrect; while consumer demand did rise post-rationing, it was not the primary driver of inflation during the war years. Option B is also wrong, as manufacturing actually increased during the war to meet military needs. Option D misrepresents the labor market; wages generally rose due to high demand for workers, not decreased. Thus, government spending for defense was the key factor in driving inflation during this period.
Which statement from the passage is an opinion?
- A. "The ill-advised rush to extract new discoveries of shale oil and natural gas is a case in point."
- B. "...if the result is polluted water and ghost towns, it is not a sustainable model."
- C. “‘Sustainability' means using natural resources responsibly so that they are available to future generations."
- D. "... to achieve sustainability a business will not view profit only in terms of dollars."
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: A
Option A expresses a subjective viewpoint about the extraction of shale oil and natural gas, labeling it as "ill-advised." This indicates a personal judgment rather than an objective fact. In contrast, Option B presents a consequence of unsustainable practices, framing it as a logical outcome rather than an opinion. Option C defines "sustainability" in a factual manner, outlining its meaning without personal bias. Lastly, Option D describes a business approach towards sustainability, focusing on a principle rather than expressing a personal belief. Thus, A stands out as the only statement rooted in opinion.
Option A expresses a subjective viewpoint about the extraction of shale oil and natural gas, labeling it as "ill-advised." This indicates a personal judgment rather than an objective fact. In contrast, Option B presents a consequence of unsustainable practices, framing it as a logical outcome rather than an opinion. Option C defines "sustainability" in a factual manner, outlining its meaning without personal bias. Lastly, Option D describes a business approach towards sustainability, focusing on a principle rather than expressing a personal belief. Thus, A stands out as the only statement rooted in opinion.
Which conclusion can be drawn from the diagrams?
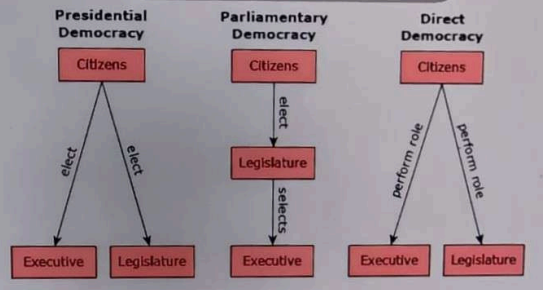
- A. The legislature is more representative of the people in a presidential democracy than in a parliamentary democracy.
- B. The branches of government are more independent of each other in a presidential democracy than in a parliamentary democracy.
- C. The executive branch is more accountable to the people in a parliamentary democracy than in a direct democracy.
- D. The people are more involved in governing in a presidential democracy than in a direct democracy.
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: B
In a presidential democracy, the separation of powers is a key feature, allowing the executive, legislative, and judicial branches to operate independently. This independence enhances checks and balances, ensuring that no single branch can dominate. Option A is incorrect as both systems aim for representation, but the degree can vary based on specific contexts rather than the type of democracy. Option C misrepresents accountability; in parliamentary systems, the executive is directly accountable to the legislature, which is elected by the people. Option D is misleading; in a direct democracy, citizens have direct involvement in governance, often more so than in a presidential system.
In a presidential democracy, the separation of powers is a key feature, allowing the executive, legislative, and judicial branches to operate independently. This independence enhances checks and balances, ensuring that no single branch can dominate. Option A is incorrect as both systems aim for representation, but the degree can vary based on specific contexts rather than the type of democracy. Option C misrepresents accountability; in parliamentary systems, the executive is directly accountable to the legislature, which is elected by the people. Option D is misleading; in a direct democracy, citizens have direct involvement in governance, often more so than in a presidential system.